

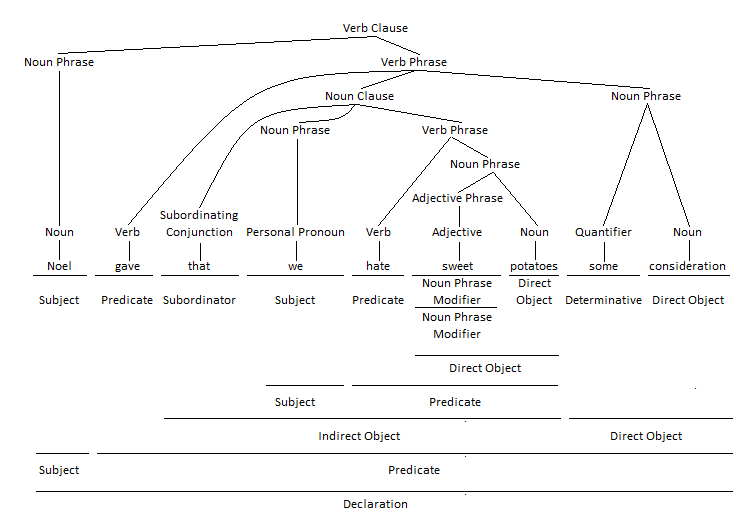
Clauses are grammatical structures that consist of a subject and a predicate. Dependent or subordinate clauses are clauses that cannot function independently as complete sentences but that must appear with another independent or main clause. Noun clauses are a type of dependent clause that perform nominal functions.
In grammar, an indirect object is word, phrase, or clause that indicates to or for whom or what the action of a ditransitive verb is performed. In addition to nouns and pronouns, noun clauses also perform the grammatical function of object complement. Examples of noun clauses as indirect objects include the following:
Noun Clause as Indirect Object
Brinton, Laurel J. & Donna M. Brinton. 2010. The linguistic structure of Modern English, 2nd edn. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company.
Hopper, Paul J. 1999. A short course in grammar. New York: W. W. Norton & Company.
Huddleston, Rodney. 1984. Introduction to the grammar of English. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.